AI Agent¶
Description¶
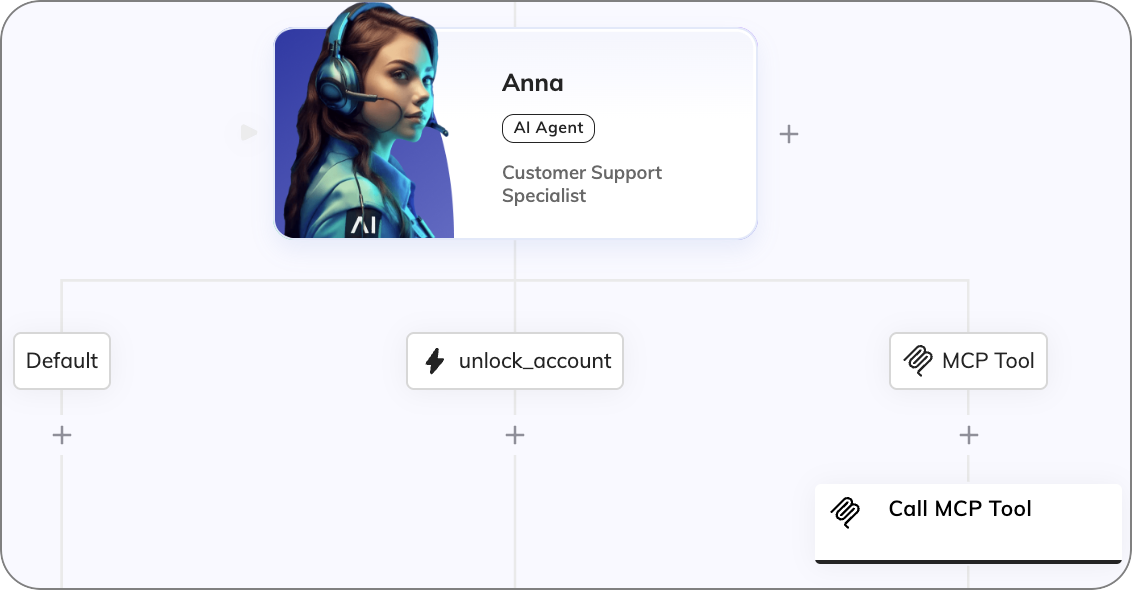
The AI Agent Node assigns a job to an AI Agent, provides instructions and tool actions for that job, and access to the knowledge the AI Agent can use when holding a conversation with a user.
To configure this Node, follow these steps:
AI Agent Settings¶
This configuration assigns a job to an AI Agent, defines its role and responsibilities, and provides additional instructions or context to guide its actions.
AI Agent
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AI Agent | Selector | Select the AI Agent. |
| Job Name | CognigyScript | Specify the name of the job. For example, Customer Support Specialist. |
| Job Description | CognigyScript | Provide a description of the job responsibilities to guide the AI Agent's interactions. For example, Assist customers with product issues, escalate complex cases, and provide guidance on best practices. |
| Instructions and Context | Toggle | Add specific instructions or context as a system message to help the AI Agent better fulfill the job requirements. For example, Stay professional and friendly; focus on problem-solving and clarity. These instructions are considered in addition to those specified in the AI Agent creation settings. |
Memory Handling
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Long-Term Memory Injection | Selector | Allow the AI Agent to access Contact Profile information for the current user. Select one of the following options:
|
| Selected Profile Fields | Text | The parameter appears when the Inject selected Profile fields option is enabled. Enter specific fields from the Contact Profile for targeted data use. Specify the field using the Profile keys format and press Enter to apply it. |
| Short-Term Memory Injection | CognigyScript | Specify a static string or a dynamic value via CognigyScript to make available to the AI Agent in the current turn. |
Grounding Knowledge
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Injection | Selector | Use the Knowledge AI feature for the AI Agent. Select one of the following options:
|
| Use AI Agent Knowledge | Toggle | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. Enable to use the Knowledge Store configured in the AI Agent. The Knowledge Store configured within the AI Agent creation settings will be used. |
| Use Job Knowledge | Toggle | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. Enable this option to configure a specific Knowledge Store for this particular job, allowing the AI Agent to access job-specific data or resources. |
| Job Knowledge Store | Selector | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. The parameter appears when the Use Job Knowledge option is enabled. Select a specific Knowledge Store for this AI Agent's job. |
| Top K | Slider | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. Specify how many knowledge chunks to return. Providing more results gives the AI Agent additional context, but it also increases noise and token usage. |
| Source Tags | CognigyScript | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. The tags serve to refine the scope of your knowledge search, allowing you to include only the most pertinent sections of the knowledge base and, as a result, improve the accuracy of search outputs. Before specifying tags, ensure that they were provided during the creation of the Knowledge Sources. Add Tags by specifying each Tag separately and pressing Enter. The maximum number of tags is 5. When you specify multiple Source Tags, the Search Extract Output Node defaults to an AND operator, meaning it only considers Sources that have all the specified Tags. This approach ensures the search results are precise and highly relevant to the end user's query. To change this behavior, go to the Match Types for Source Tags parameter. |
| Match type for Source Tags | Select | The parameter appears when you select either When Required or Once for Each User Input. The operator to filter Knowledge Sources by Source Tags. Select one of the following options:
|
| Generate Search Prompt | Toggle | The parameter appears when you select Once for Each User Input. This parameter is enabled by default and allows you to generate a context-aware search prompt before executing the knowledge search. Note that enabling this parameter may lead to increased cost and latency. |
Storage and Streaming Options
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| How to handle the result | Select | Determine how to handle the prompt result:
|
| Input Key to store Result | CognigyScript | The parameter appears when you select either Store in Input or Stream to Output. The result is stored in the input.aiAgentOutput object by default. You can specify another value, but the AI Agent Output Token will not work if the value is changed. |
| Context Key to store Result | CognigyScript | The parameter appears when Store in Context is selected. The result is stored in the context.aiAgentOutput object by default. You can specify another key. |
| Stream Buffer Flush Tokens | Text Array | The parameter appears when Stream to Output is selected. It defines tokens that trigger the stream buffer to flush to the output. The tokens can be punctuation marks or symbols, such as \n. |
| Output result immediately | Toggle | The parameter appears when you select either Store in Input or Store in Context. This parameter allows you to output results immediately without using the Say Node and AI Agent Output token. |
| Store Copy in Input | Toggle | The parameter appears when Stream to Output is selected. In addition to streaming the result to the output, store a copy in the Input object by specifying a value in the Input Key to store Result field. |
Voice
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Voice Setting | Select | Configure the voice settings for the AI Agent Job. This parameter determines how the AI Agent selects the voice for text-to-speech (TTS) output. Select one of the following options: - Inherit from AI Agent — use the voice settings defined in the AI Agent creation settings. - Use Job Voice – apply custom voice settings specific to this job, allowing the AI Agent to adapt to the particular role it performs. For example, if you create a marketing AI Agent, the voice can be more engaging, friendly, and persuasive. However, if the same AI Agent performs a different role, such as customer support, the voice might be more neutral, empathetic, and formal. |
| TTS Vendor | Dropdown | Select a TTS vendor from the list or add a custom one. Note that the AI Agent Node doesn't support TTS Labels to distinguish configurations from the same TTS vendor. To use TTS Labels, add a Set Session Config Node before the AI Agent Node in the Flow editor. |
| Custom (Vendor) | CognigyScript | The Custom parameter appears when you select Custom from the TTS Vendor list. Specify the custom TTS Vendor. For preinstalled providers, use all lowercase letters, for example, microsoft, google, aws. For custom providers, use the name that you specified on the Speech Service page in the Voice Gateway Self-Service Portal. |
| TTS Language | Dropdown | Define the language of the voice AI Agent output. Ensure this language aligns with the preferred language of the end user. |
| Custom (Language) | CognigyScript | The Custom parameter appears when you select Custom from the TTS Language list. Specify the language of the AI Agent output. The format depends on the option selected in the TTS vendor; check your TTS vendor documentation. The typical format is as follows: de-DE, fr-FR, en-US. |
| TTS Voice | Dropdown | Define the voice that should be used for the voice AI Agent output. This parameter allows you to customize the AI Agent's voice by defining its tone, gender, style, and regional specifics, making conversations more personalized and aligned with your brand and target audience. |
| Custom (Voice) | CognigyScript | The Custom parameter appears when you select Custom from the TTS Voice list. Use this parameter to specify a custom voice, which is often required for region-specific voices. The format depends on the option selected in TTS Vendor and typically follows the pattern language-region-VoiceName. For example, de-DE-ConradNeural for German (Germany) male voice or en-US-JennyNeural for English (US) female voice. |
| TTS Label | CognigyScript | The alternative name of the TTS vendor is the one you specify in the Voice Gateway Self-Service Portal. If you have created multiple speech services from the same vendor, use the label to specify which service to use. |
| Disable TTS Audio Caching | Toggle | Disables TTS audio caching. By default, the setting is deactivated. In this case, previously requested TTS audio results are stored in the AI Agent cache. When a new TTS request is made and the audio text has been previously requested, the AI Agent retrieves the cached result instead of sending another request to the TTS provider. When the setting is activated, the AI Agent caches TTS results but doesn't use them. In this case, each request is directly sent to your speech provider. Note that disabling caching can increase TTS costs. For detailed information, contact your speech provider. |
Tool Settings
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Choice | Selector | If supported by your LLM Model, this will determine how tools should be selected by the AI Agent:
|
| Use Strict mode | Toggle | When the parameter is enabled, strict mode (if supported by the LLM provider) ensures that the arguments passed to a tool call precisely match the expected parameters. Enabling this feature can help prevent errors. However, it may cause a slight delay in the response, especially during the first call after making changes. |
Image Handling
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Process Images | Toggle | Enable the AI Agent to read and understand images attachments. Make sure that your LLM provider supports image processing; refer to your provider's documentation. In addition, make sure that attachments are supported by and activated in your Endpoint, for example, Webchat. |
| Images in Transcript | Selector | Configure how images older than the last turn are handled to reduce token usage:
|
Advanced
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LLM | Selector | Select a model that supports the AI Agent Node feature. The selected Default model is the model that you specified in Settings > Generative AI Settings of your Project. Select the model that you added earlier while configuring Agentic AI feature. This model will manage your AI Agent. |
| AI Agent Base Version | Selector | Select the base version of the AI Agent to use:
When upgrading to a fixed version or switching to the latest, always test your AI Agent carefully to ensure it works with the selected version. |
| Timeout | Number | Define the maximum number of milliseconds to wait for a response from the LLM provider. |
| Maximum Completion Tokens | Slider | Define the maximum number of tokens that can be used during a process to manage costs. However, if the limit is set too low, the output may be incomplete, as the process could be cut off before it finishes. For example, if you set the maximum tokens to 100, the model will stop generating content once it reaches 100 tokens. This number would be roughly equal to 100 words, depending on the language and tokenization method. |
| Temperature | Slider | Define the sampling temperature, which ranges between 0 and 1. Higher values, such as 0.8, make the output more random, while lower values, such as 0.2, make it more focused and deterministic. |
Error Handling
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log to System Logs | Toggle | Log errors to the system logs. They can be viewed on the Logs page of your Project. The parameter is inactive by default. |
| Store in Input | Toggle | Store errors in the Input object. |
| Select Error Handling Approach | Select | You can select one of the Error Handling options:
|
| Select Flow | Select | The parameter appears when Go to Node is selected. Select a Flow from the available options. |
| Select Node | Select | The parameter appears when Go to Node is selected. Select a Node from the available options. |
| Error Message (optional) | CognigyScript | Add the optional message to the output if the AI Agent Node fails. |
Debug Settings
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log Job Execution | Toggle | Send a debug message with the current AI Agent Job configuration. The message appears in the Interaction Panel when debug mode is enabled. The parameter is active by default. |
| Log Knowledge Results | Toggle | Send a debug message containing the result from a knowledge search. The message appears in the Interaction Panel when debug mode is enabled. The parameter is inactive by default. |
| Show Token Count | Toggle | Send a debug message containing the input, output, and total token count. The message appears in the Interaction Panel when debug mode is enabled. Cognigy.AI uses the GPT-3 tokenizer algorithm, so actual token usage may vary depending on the model used. The parameter is inactive by default. |
| Log System Prompt | Toggle | Send a debug message containing the system prompt. The message appears in the Interaction Panel when debug mode is enabled. The parameter is inactive by default. |
| Log Tool Definitions | Toggle | Send a debug message containing information about the configured AI Agent tools. The message appears in the Interaction Panel when debug mode is enabled. The parameter is inactive by default. |
AI Agent Tool Settings¶
Tool actions are child Nodes of AI Agent Nodes. They define actions that can be taken by the AI Agent. If an AI Agent wants to execute the tool, the branch below the child Node is executed.
At the end of a tool action branch, it is advisable to use a Resolve Tool Action Node to return to the AI Agent.
Clicking the Tool Node lets you define a tool, set its parameters, and allows debugging by enabling detailed messages about the tool's execution.
Tool
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tool ID | CognigyScript | Provide a meaningful name as a Tool ID. This ID can contain only letters, numbers, underscores (_), or dashes (-). For example, update_user-1. |
| Description | CognigyScript | Provide a detailed description of what the tool does, when it should be used, and its parameters. |
Parameters
Configure the parameters that will be collected by the AI Agent before the tool is called. You can switch between the Graphical and JSON editors. When editing the JSON, follow the JSON Schema specification.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Use Parameters | Toggle | Activate this toggle to add parameters in addition to the tool name and description. The AI Agent will collect all data it needs and call a Tool with these parameters filled as arguments. These values can be accessed directly in the input.aiAgent.toolArgs object. |
| Name | Text | Specify the name of the parameter. The name should be clear and concise, and describe the purpose of the parameter. |
| Type | Selector | Select a type of the parameter:
|
| Description | CognigyScript | Explain what parameter means by providing a brief description of the parameter's usage. |
| Enum (optional) | Enum | Define a set of values that the parameter can accept. The enum restricts the input to one of the specified values, ensuring only valid options are chosen. The enum is only available for string-type parameters in the Graphical editor. For other types, use the JSON editor. May not be supported by all LLM providers. |
| Add Parameter | Button | Add a new parameter. |
Debug Settings
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Debug Message when called | Toggle | Enable the output of a debug message when the tool is called to provide detailed information about the tool call. |
Advanced
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Condition | CognigyScript | The tool will be enabled only if the condition is evaluated as true. If false, the tool isn't part of the AI Agent's Tools within this execution. For example, when using the unlock_account tool, you can specify a condition likecontext.accountStatus === "locked"`. This checks the value in the context, and if it is missing or different, the tool will not be enabled. |
AI Agent MCP Tool Settings¶
MCP Tool Nodes are child Nodes of AI Agent Nodes. The MCP Tool Nodes connect to a remote MCP server to load tools that the AI Agent can execute. If an AI Agent wants to execute one of the loaded tools, the branch below the MCP Tool Node is triggered.
Clicking the MCP Tool Node lets you define the connection, filter loaded tools, and allows debugging by enabling detailed messages about the tool's execution.
MCP Tool
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | CognigyScript | Provide a name for the MCP connection. This name helps you identify the source of the loaded tool. |
| MCP Server SSE URL | CognigyScript | Provide the URL to an SSE (Server-Sent Events) endpoint from a remote MCP server. Ensure that you connect only to trusted MCP servers. |
| Timeout | Slider | Set the timeout time for the MCP connection in seconds. |
Debug Settings
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Debug loaded Tools | Toggle | Enable this parameter to display a debug message with all tools loaded from the MCP server. The debug message also includes tools that have been filtered out in the Advanced section. |
| Debug with Parameters | Toggle | Enable this parameter to include the Tool Parameters in the debug message. |
| Debug calling Tool | Toggle | Enable the output of a debug message when the tool is called to provide detailed information about the tool call. |
Advanced
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cache Tools | Toggle | Disable caching of loaded tools while developing. Ensure that caching is enabled in production for performance reasons. The caching time is 10 minutes. |
| Condition | CognigyScript | The tool will be enabled only if the condition is evaluated as true. If false, the tool isn't part of the AI Agent's Tools within this execution. For example, when using the unlock_account tool, you can specify a condition likecontext.accountStatus === "locked"`. This checks the value in the context, and if it is missing or different, the tool will not be enabled. |
| Tool Filter | Select | Control tool filtering by selecting one of the following options: - None — no tool filtering is applied, and all tools are available for execution. This option is selected by default. - Whitelist — only tools on the list are allowed for execution, while all other tools are excluded. - Blacklist — tools on the list are excluded from execution, while all other tools remain available. |
| Blacklist | CognigyScript | The parameter appears if you select Blacklist in Tool Filter. Specify the tools that should be blocked from execution. Specify only one tool per field. |
| Whitelist | CognigyScript | This parameter appears if you select Whitelist in Tool Filter. Specify the tools you want to allow for execution. Specify only one tool per field. |
Call MCP Tool Settings¶
In the Flow editor, when you add an MCP Tool Node, a Call MCP Tool Node is automatically created below it. These two Nodes work together to define and execute the chosen tool. The Call MCP Tool Node sets the actual execution point of the chosen tool. This way, you can verify or modify teh tool call arguments in the input.aiAgent.toolArgs object, or add a Say Node before the tool call. When the Call MCP Tool Node is executed, the tool call is sent to the remote MCP server, where the Tool is executed remotely with any arguments set by the AI Agent.
To return the tool result to the AI Agent, the Resolve Immediately setting can be enabled to send the full result returned from the remote MCP server to the AI Agent.
As an alternative, use a Resolve Tool Action Node to return a specific result to the AI Agent.
Call MCP Tool
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Resolve Immediately | Toggle | Enable this parameter to immediately resolve the tool action with the full result as the tool answer. |
Storage Options
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| How to handle the result | Select | Determine how to handle the MCP tool call result:
|
| Input Key to store Result | CognigyScript | The parameter appears when Store in Input is selected. The result is stored in the input.aiAgent.toolResult object by default. You can specify another value, but the MCP Tool Result Token won't work if the value is changed. |
| Context Key to store Result | CognigyScript | The parameter appears when Store in Context is selected. The result is stored in the context.aiAgent.toolResult object by default. |
Debug Settings
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Debug Tool Result | Toggle | Enable the output of a debug message with the tool call result after a successful call. |
Examples¶
AI Agent Tool¶
In this example, the unlock_account tool unlocks a user account by providing the email and specifying the reason for the unlocking.
Parameter configuration in JSON:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "string",
"description": "User's login email for their account."
}
},
"required": ["email"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
where:
type— the type for a tool parameter schema, which must always beobject.properties— defines the parameters for the tool configuration:email— a required tool parameter for unlocking the account.type— defines the data type for the tool parameter.description— a brief explanation of what the property represents.
required— listsemailas a required parameter, ensuring that this value is always provided when the tool is called.additionalProperties— ensures that the input contains only theemailtool parameter, and no others are allowed.
AI Agent MCP Tool and Call MCP Tool¶
Use Zapier's Remote MCP server¶
You can create a custom MCP server with personalized tools by using one of the provided SDKs. For a quicker setup, you can use a third-party provider. For example, Zapier allows you to configure your MCP server, which can be connected to multiple application APIs.
To use Zapier as a remote MCP server, follow these steps:
- Log in to your Zapier account, go to the MCP settings page, and configure your MCP server.
- Copy the SSE URL and paste it into the MCP Server SSE URL field of your MCP Tool Node.
- In the Zapier MCP settings, create an action to connect to various APIs. For example, you can create a Zapier action to automatically generate a Google Doc.
Once the setup is complete, the configured MCP Actions will be loaded when the AI Agent is executed.
You will see the following debug message in the Interaction Panel, indicating the result of the tool call after a successful execution:
AI Agent: MCP Tool
Fetched tools from MCP Tool "zapier"
- google_docs_create_document_from_: Create a new document from text. Also supports limited HTML.
Parameters:
- title (string): Document Name
- file (string): Document Content
