Knowledge AI¶
Note
- You are subject to the terms of the Generative AI model providers you are using. Cognigy doesn't take responsibility for your use of third-party services, systems, or materials.
- If you are a Cognigy customer, the performance timelines (SLA) specified in your contract do not apply to the trial version of Knowledge AI.
Knowledge AI is a knowledge search and management solution that uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to improve AI Agents' performance and assist human agents. Knowledge AI applies RAG to provide AI Agents with access to a large amount of structured information from different files in a knowledge base, such as articles, manuals, FAQs, and more. By accessing the knowledge base, AI Agents can retrieve and understand specific information, and provide more accurate, context-aware, and helpful responses to user queries.
With Knowledge AI, you have more options beyond relying on Intents and Default Replies to identify user questions and provide relevant content based on predefined questions and answers. Creating question-and-answer pairs can be time-consuming and require labor-intensive maintenance.
Knowledge AI lets you upload knowledge in various formats, such as PDF, Cognigy Text (CTXT) and web pages, as Knowledge Sources. This technology extracts meaningful information from these documents and makes it accessible to conversation designers through the Search Extract Output Node. With this Node, you can build knowledge-based AI Agents quickly, overcoming the limitations of traditional intent-based systems and simplifying the creation of sophisticated conversational experiences.
Prerequisites¶
Before using Knowledge AI, follow these steps:
- Apply for a license and allocate quotas.
-
Get access to an account from one of the following LLM Providers:
Which Models to Choose?¶
To use the full potential of Knowledge AI, you need:
-
An embedding model to convert information from documents into embeddings in Knowledge Sources and perform Knowledge Searches. Knowledge AI supports the following embedding models:
Model Comment text-embedding-ada-002– text-embedding-3-smallThe model may be available only in geographically remote locations, leading to high latency for the search operation. text-embedding-3-largeThe model may be available only in geographically remote locations, leading to high latency for the search operation. The model outputs embedding vectors twice as large as those from text-embedding-ada-002andtext-embedding-3-small. Larger embedding vectors result in higher memory usage and larger Package sizes for Knowledge AI.amazon.titan-embed-text-v2:0For Cognigy.AI 2025.10 and earlier versions, use the FEATURE_ENABLE_AWS_BEDROCK_EMBEDDING_LLM_WHITELISTenvironment variable to make this model available to individual or all feature flags. -
A generative model that supports LLM Prompt Nodes or Answer Extraction to use Knowledge Search results to generate context-aware response to user questions.
Once a model is set up within a Project, all other Knowledge Stores will use the same model. If you want to switch to a different model, you must either delete all existing Knowledge Stores in the current Project or create a new Project.
Knowledge Management¶
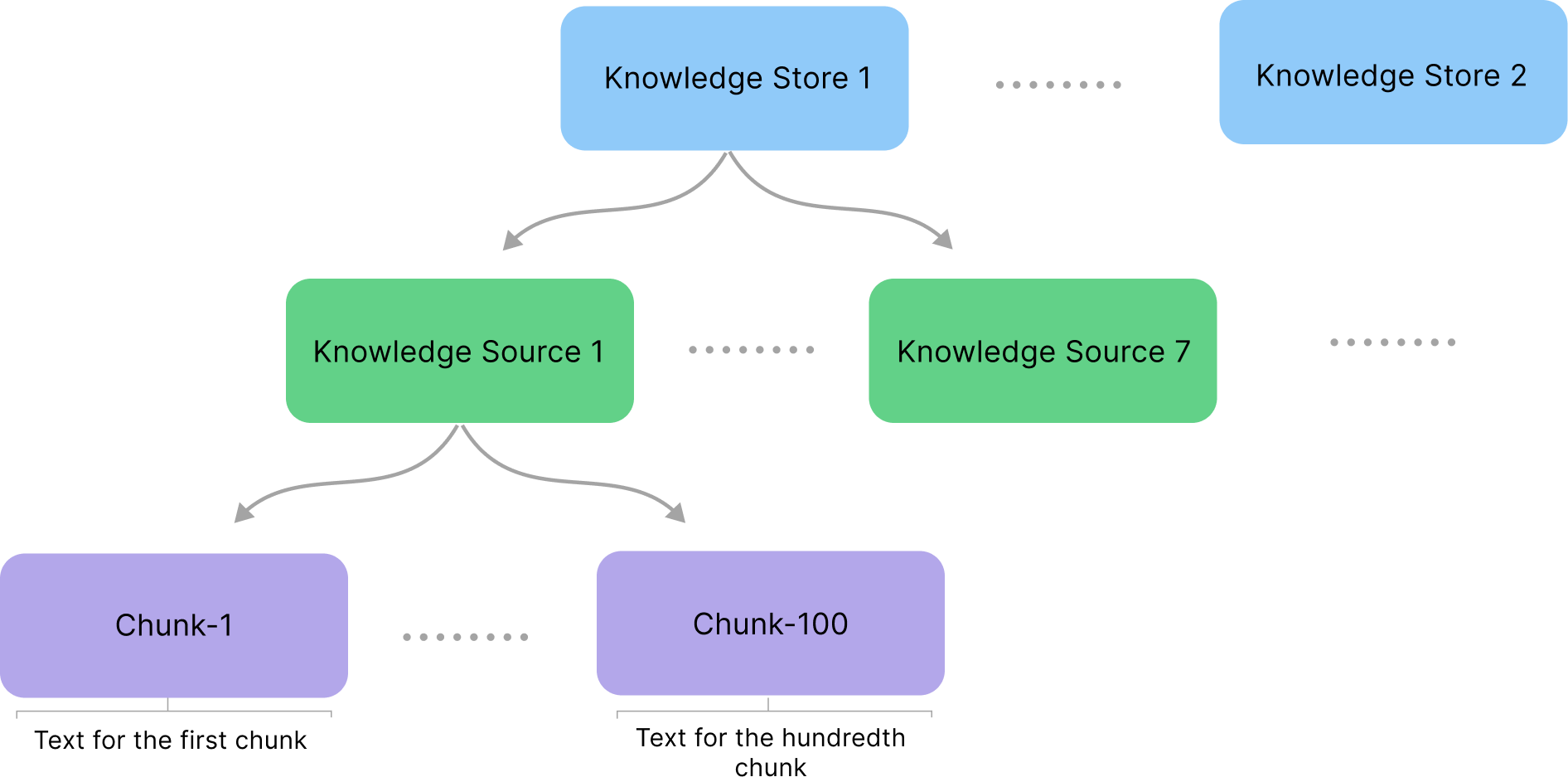
Knowledge AI has the following knowledge hierarchy:
- Knowledge Store — a container that includes Knowledge Sources.
- Knowledge Source — a collection of organized and structured knowledge extracted from files, for example, user manuals, articles, FAQs, and other relevant information.
- Knowledge Chunk — a unit of knowledge inside a Knowledge Source.
Knowledge AI Workflow¶
Working with Knowledge AI involves two phases, similar to the Intents workflow. The first phase consists of collecting, preprocessing, and integrating data — a process known as ingestion — from your knowledge base, and the second phase is querying the knowledge base during run-time.
First Phase¶
- Raw Information Upload — you upload information as files to Knowledge AI.
- Knowledge Chunk Extraction — Knowledge AI extracts text and metadata from the raw information through a collection of tools and processes the information into a Knowledge Source. The Knowledge Source is divided in Knowledge Chunks, which you can edit in the Chunk editor.
- Vectorization — Knowledge AI encodes Knowledge Chunks into embeddings. Embeddings are high-dimensional vectors that encode word meaning and similarity into numeric representations. Knowledge AI stores the embeddings in a specialized internal database for quick access during run-time.
Second Phase¶
- Knowledge Base Querying. During run-time, Knowledge AI queries the Knowledge Sources to provide accurate and contextually appropriate responses to user questions.
- Knowledge-based AI Agents Building. AI Agents use the information stored in the Knowledge Sources to engage in more sophisticated and intelligent conversations with users.
Use cases¶
With Knowledge AI, both human agents and AI Agents can retrieve information from various Knowledge Sources and provide better responses to your customers:
- Knowledge AI for AI Agents — use the Search Extract Output Node so that AI Agents can retrieve product-specific knowledge from Knowledge Sources, for example, manuals and web pages. This way, AI Agent's output more accurate information to customers.
- Use Knowledge AI for human agents — by retrieving data from different Knowledge Sources, LLMs reduce the burden on human agents, making information access quicker and more efficient. To let human agents use the Knowledge Sources for solving tasks, add a widget to the Agent Copilot workspace using a Copilot: Knowledge Tile Node. The widget serves as a search tool, enabling human agents to enter questions and retrieve information from the knowledge base.
FAQ
Q1: Is Knowledge AI free of charge?
A1: Knowledge AI is not free of charge and requires a separate license.
Q2: I received Request failed with status code 429 error message while attempting to upload a file. How can I solve this issue?
A2: The 429 error occurs when your organization's rate limit is exceeded on the side of your LLM's provider. To learn more, refer to your provider's documentation. For instance, if you use the OpenAI API, check out the article How can I solve 429: 'Too Many Requests' errors?.
Q3: I received a Error while performing knowledge search. Remote returned error: Search failed: Could not fetch embeddings due to missing API resource name for Azure OpenAI error message while using knowledge search features. How can I solve this issue?
A3: In recent releases, we have updated the connection settings to Azure OpenAI LLMs and added new parameters, such as the Resource Name. If you have an older connection (for example, created in the 4.53 release) to Azure OpenAI LLMs, especially Azure OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 for Knowledge Search, you might receive this error message when you trigger an LLM. To resolve this issue, recreate the LLM and the connection so that both have the latest format.
